
Across all industries, the buzz about Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) and ChatGPT is hard to ignore. In 2024, we urge you to understand these tools and recognize how they will shape the future of your role and business.
Definitions
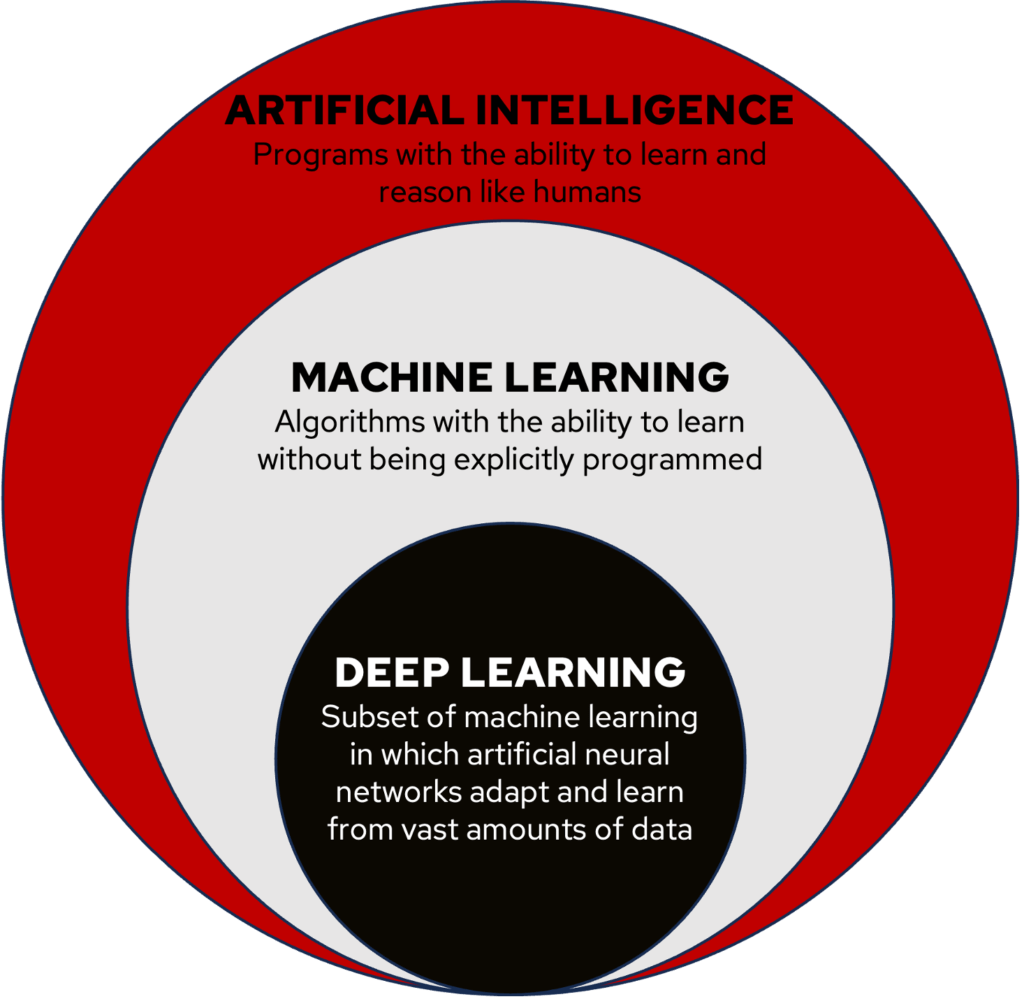
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Computer systems that mimic human intelligence for learning, pattern analysis, and decision making from data.
Machine Learning (ML): Algorithms with the ability to learn from data.
Deep Learning: A subset of machine learning in which artificial neural networks adapt and learn from vast amounts of data.
Data Science: Data analysis plus the application of machine learning in a principled way, usually on huge datasets.
Applications
AI is used as extensively as computers – basically, everywhere! It is applied wherever large datasets can be used for classifying information into categories or predicting future behavior.
AI/ML leverages data collected across a wide range of circumstances to predict other behavior, factoring in vast numbers of inputs over a range of operating conditions. AI and the data it uses enable us to create high-dimensional models rather than single points of information. In addition, it is also well suited for classification or pattern matching tasks given enough training data.
Consider where you use computers, and you will find applications for AI, such as healthcare, banking, transportation, navigation, social media, robotics, factory floor automation, marketing, cybersecurity, and beyond.
Why now?
The increasing volume and variety of data, combined with improved computational processing capabilities, affordable data storage and availability of open-source software libraries and frameworks, combine to create broad accessibility to AI/ML. Many businesses are just now beginning to realize the value of their data.
Tools that allow people to use AI/ML without fully understanding how those tools explicitly work have recently been launched which provide a virtual assistant-type of functionality, such as GPT4, Microsoft Copilot, Bing Chat and Bard.
These tools are all large language models (LLMs) that predict the next best word(s) to a prompt of words.
Next steps
As AI/ML shape increasing amounts of the information around us, it is important for managers and technical professionals to:
- Understand what AI/ML tools are good at and what they are bad at
- Understand the pitfalls, limitations, and potential of AI/ML
- Make decisions about how/why to use AI/ML in their workplace
- Appreciate how AI/ML can filter and use data that already exists to provide competitive advantage or reduce costs
Explore these topics and more in our synchronous online course, Foundations of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, taught by world renowned AI expert, Dr. Barry Van Veen.